Helicopters have undergone significant evolution since their inception, diversifying into specialized types tailored for military, civilian, and niche
Helicopters have undergone significant evolution since their inception, diversifying into specialized types tailored for military, civilian, and niche applications. This comprehensive guide explores the intricacies of each helicopter type, highlighting their roles, capabilities, and technological advancements.
1. Stealth Helicopters
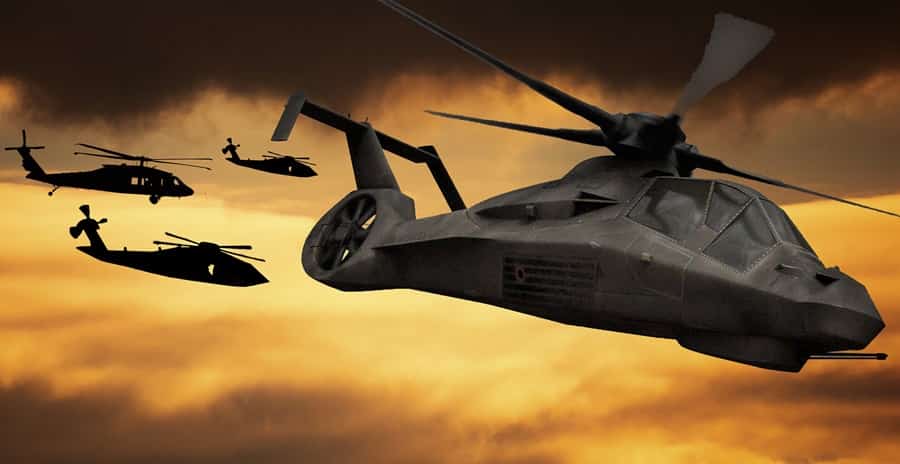

Stealth helicopters are designed with advanced technologies to reduce their radar cross-section and infrared signature, enhancing their ability to operate covertly in hostile environments. These advancements include special materials, aerodynamic designs, and noise reduction measures.
Applications: Primarily used in military operations, stealth helicopters excel in reconnaissance, special operations, and precision strikes where avoiding detection is critical. The Eurocopter Tiger and experimental models exemplify efforts to integrate stealth capabilities into rotary-wing aircraft.
2. Attack Helicopters
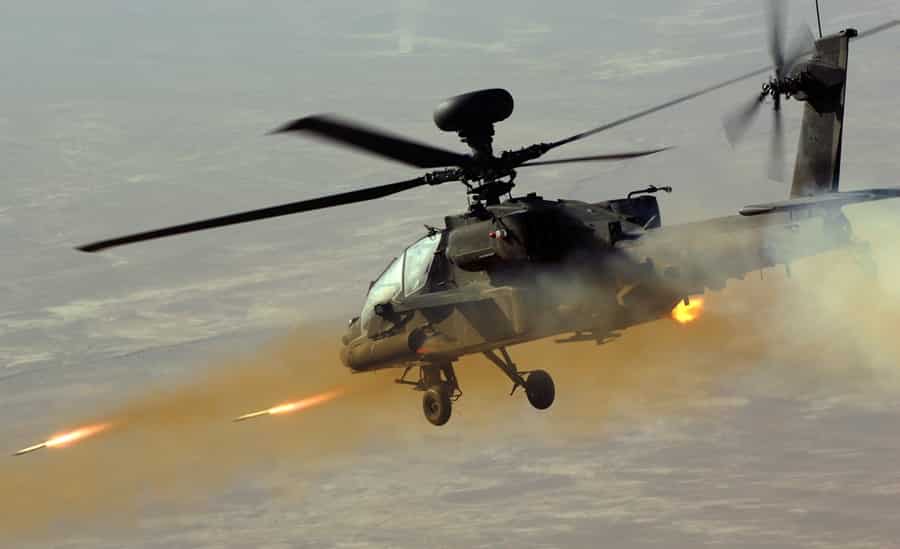

Attack helicopters are heavily armored and armed to perform direct combat missions against ground targets and enemy aircraft. They typically feature advanced targeting systems, multi-barrel cannons, rockets, and anti-tank missiles, making them formidable assets on the battlefield.
Applications: Key roles include close air support (CAS), anti-armor operations, and escort missions. Attack helicopters like the Apache AH-64 are pivotal in modern warfare for their ability to provide fire support to ground troops and engage armored vehicles effectively.
3. Tiltrotors Helicopters
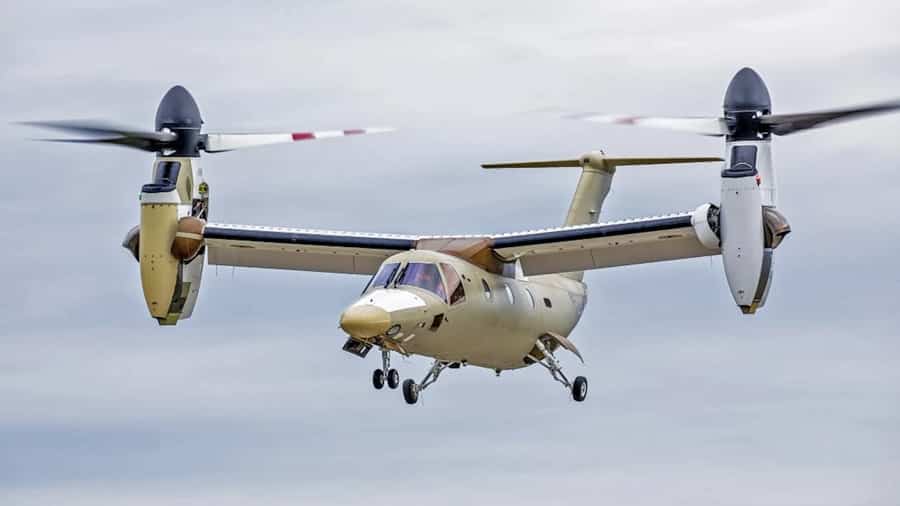

Tiltrotors combine the vertical takeoff and landing (VTOL) capabilities of helicopters with the speed and efficiency of fixed-wing aircraft. They feature rotors that tilt from vertical to horizontal positions, enabling seamless transition between helicopter and airplane modes.
Applications: Tiltrotors such as the V-22 Osprey are used in both military and civilian sectors for long-range transport, amphibious assault, and search and rescue operations. Their ability to hover like helicopters and cruise at high speeds like airplanes enhances their versatility.
4. Observation Helicopters
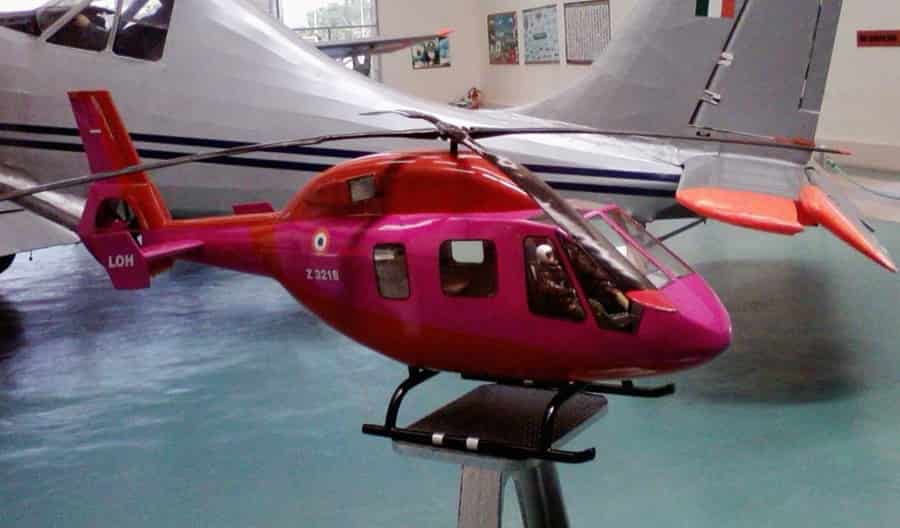

Observation helicopters are compact and agile, optimized for reconnaissance and surveillance missions. They typically carry a pilot and an observer, equipped with sensors, cameras, and communication equipment to gather real-time intelligence.
Applications: Initially developed for military reconnaissance, these helicopters now serve roles in law enforcement, border patrol, and news reporting. Their maneuverability and ability to operate at low altitudes make them invaluable for situational awareness in dynamic environments.
5. Transportation Helicopters
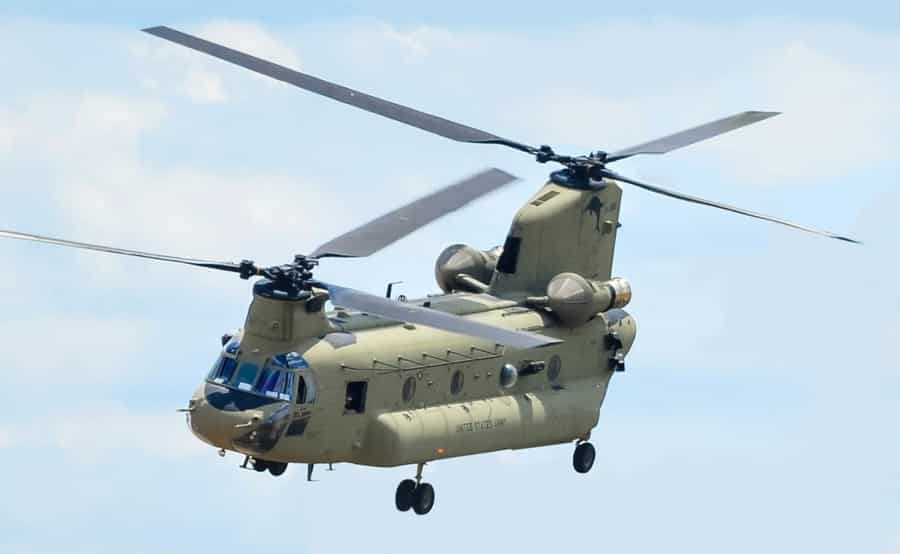

Transportation helicopters are designed for carrying passengers, cargo, or a combination of both. They range in size from small utility helicopters to large transport aircraft capable of accommodating troops, equipment, or specialized cargo.
Applications: In military settings, transportation helicopters facilitate troop movement, logistics support, and medical evacuations (MEDEVAC). In civilian use, they serve roles in aerial tourism, offshore oil rig support, and emergency medical transport, providing access to remote locations.
6. Cargo Helicopters
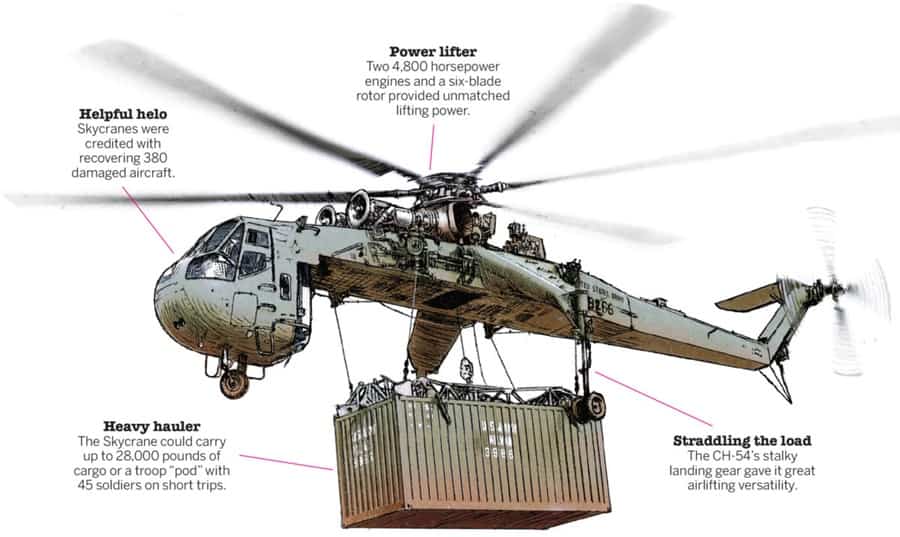
Cargo helicopters specialize in transporting heavy and oversized loads, either internally or externally. They feature robust structures, powerful engines, and specialized loading systems to handle diverse cargo types.
Applications: Essential in disaster relief efforts, cargo helicopters deliver supplies, equipment, and humanitarian aid to areas inaccessible by ground vehicles. They also support construction projects, firefighting operations, and logistical challenges where traditional transport methods are impractical.
7. Aerial Cranes
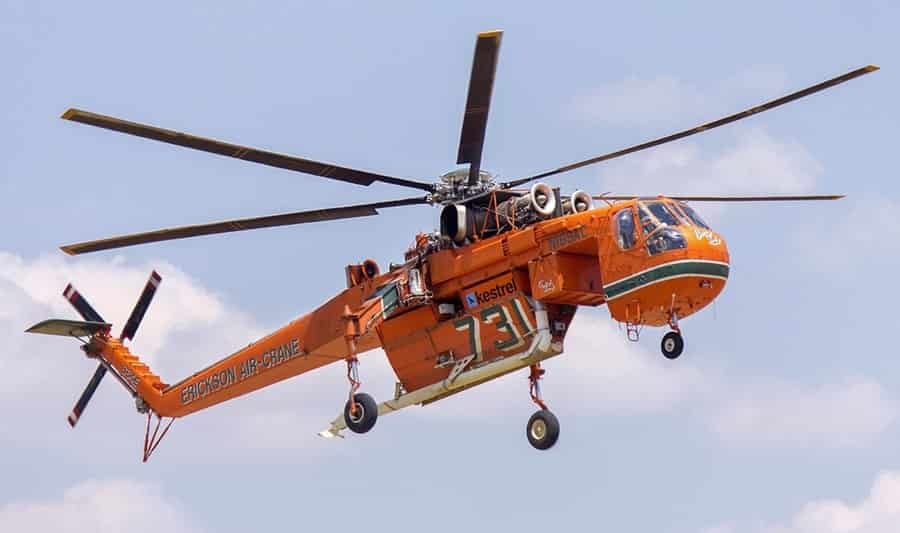

Aerial cranes are heavy-lift helicopters designed for lifting and transporting exceptionally large or heavy objects. They often feature specialized hoisting equipment, such as external hooks or cargo nets, for loading and unloading oversized cargo.
Applications: Historically used in construction, mining, and offshore operations, aerial cranes excel in lifting heavy machinery, building materials, and equipment to remote or inaccessible sites. They provide essential logistical support where ground transportation is limited.
8. Maritime Surveillance Helicopters
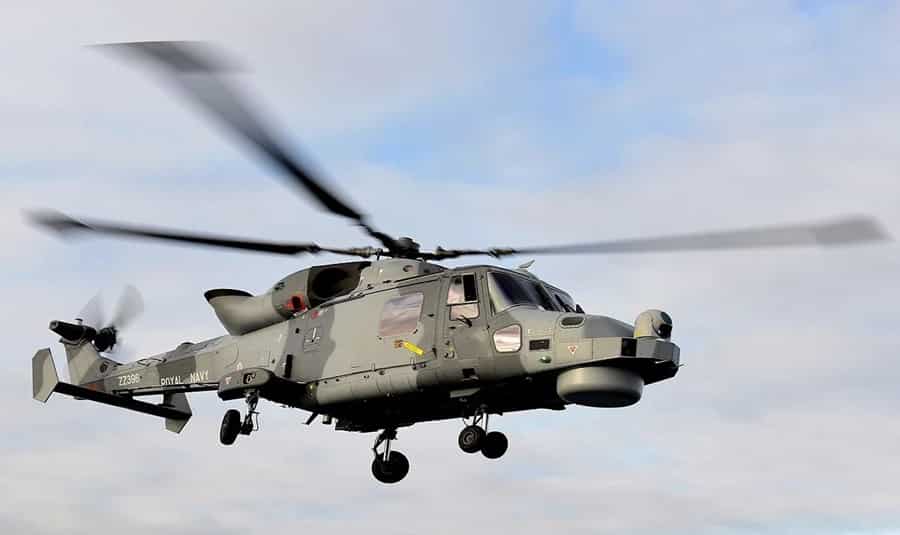

Maritime surveillance helicopters are equipped with radar, sonar, and anti-submarine warfare (ASW) capabilities to detect and track submarines and surface vessels. They operate from naval ships or shore bases to protect maritime assets and ensure sea lane security.
Applications: Vital in naval operations, these helicopters conduct anti-submarine patrols, search and rescue missions, and maritime law enforcement. They play a critical role in detecting underwater threats and safeguarding naval fleets against potential adversaries.
9. Search & Rescue Helicopters
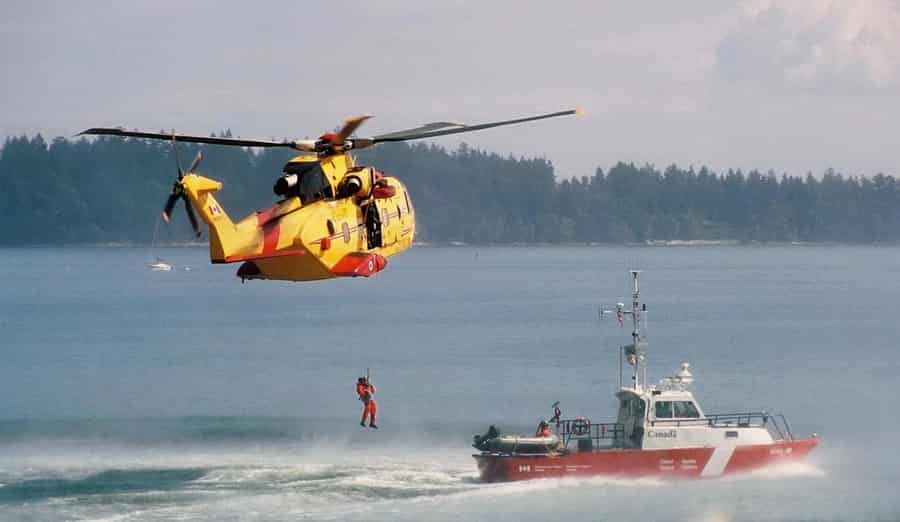

Search and rescue (SAR) helicopters are dedicated to locating and extracting individuals in distress, often in remote or hazardous environments. They feature hoists, winches, and medical equipment to perform rapid evacuations and provide emergency medical care.
Applications: Operated by military, coast guard, and civilian agencies, SAR helicopters respond to emergencies ranging from maritime incidents and mountain rescues to natural disasters and medical evacuations. Their ability to hover and maneuver in confined spaces enhances their lifesaving capabilities.
10. Aerial Refueling Helicopters
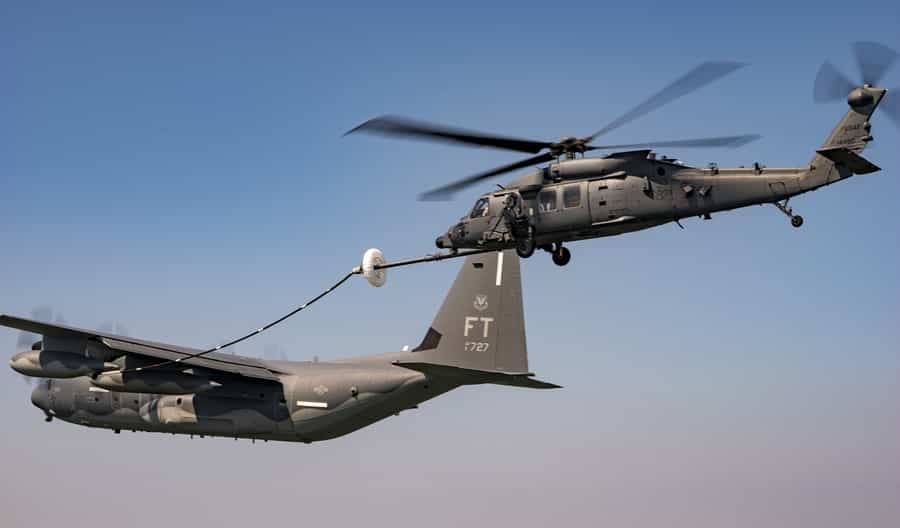

Aerial refueling helicopters support naval operations by refueling ships at sea, ensuring extended operational range and mission endurance for naval fleets. They employ specialized refueling systems and procedures for efficient fuel transfer.
Applications: Critical in maritime logistics, these helicopters provide on-demand refueling capabilities to naval vessels operating in remote or hostile waters. Ongoing developments explore their potential for aerial refueling of fixed-wing aircraft, expanding their role in military logistics.
11. Utility Helicopters
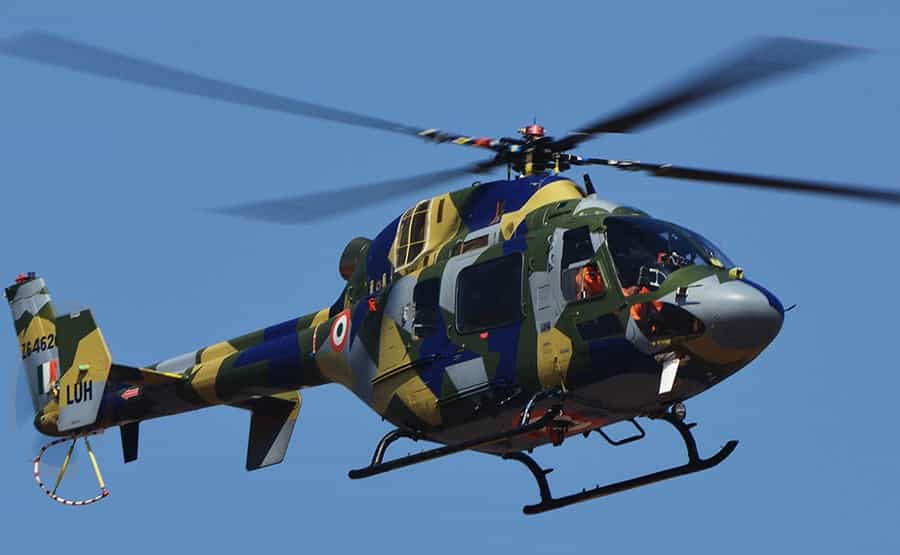

Utility helicopters are versatile platforms used for a wide range of missions including troop transport, firefighting, disaster relief, and aerial construction. They feature modular interiors and specialized equipment to adapt to diverse operational requirements.
Applications: Ubiquitous in both military and civilian sectors, utility helicopters perform essential roles from combat support and humanitarian aid to law enforcement and VIP transport. Their flexibility makes them indispensable assets in dynamic and unpredictable environments.
12. General Aviation Helicopters
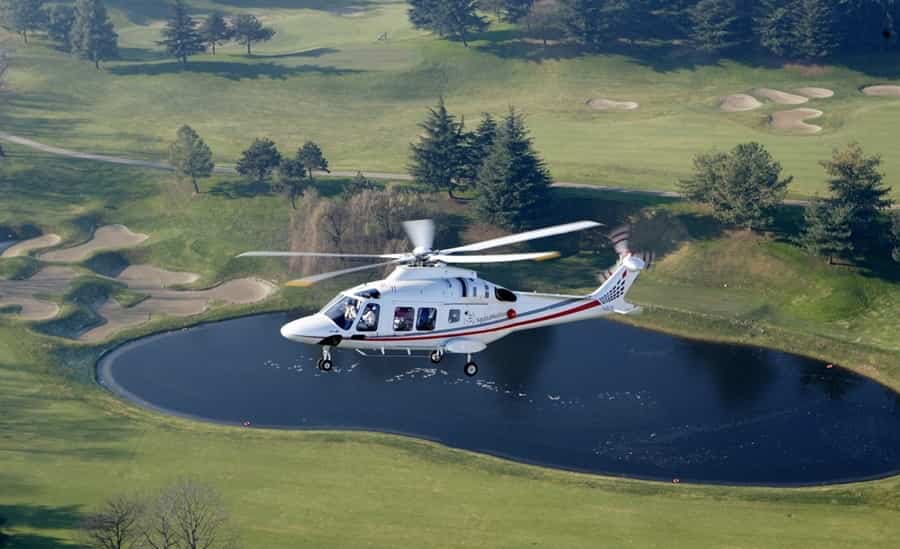

General aviation helicopters are lightweight, typically single or dual-seat aircraft used for personal transportation, aerial photography, and recreational flying. They are characterized by their compact size, maneuverability, and ease of operation.
Applications: Owned by private individuals, corporations, and flight schools, general aviation helicopters serve roles in tourism, aerial surveys, and pilot training. They provide affordable access to aerial transportation and leisure activities for enthusiasts and professionals alike.
13. MEDEVAC Helicopters
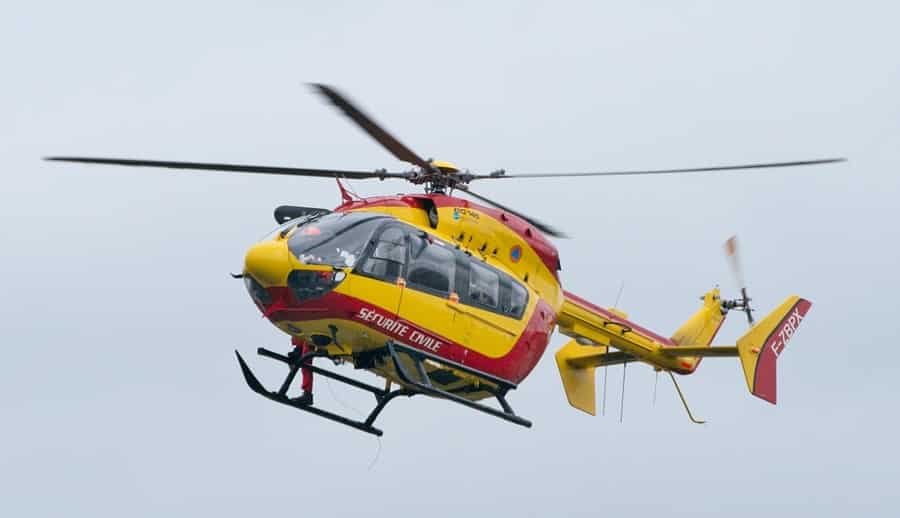

MEDEVAC helicopters are equipped with medical facilities and personnel to provide rapid evacuation and emergency medical care to injured or critically ill patients. They operate in diverse environments from urban centers to remote wilderness areas.
Applications: Essential in emergency medical services (EMS), MEDEVAC helicopters respond to accidents, medical emergencies, and natural disasters where ground transport is impractical or time-sensitive. Their swift response capability saves lives by expediting transport to definitive care facilities.
14. Luxury Helicopters
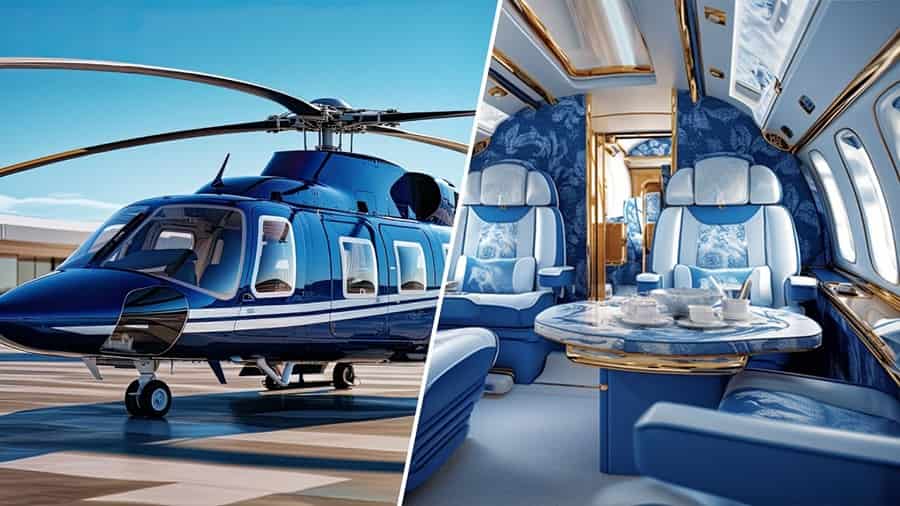

Luxury helicopters are customized with opulent interiors and amenities to cater to affluent individuals, VIPs, and corporate executives seeking exclusive airborne transport. They combine performance with lavish comfort and personalized service.
Applications: Utilized for executive travel, VIP transport, and luxury tourism, these helicopters offer prestige and convenience. Customization options from luxury brands enhance their appeal, providing a luxurious flying experience tailored to discerning clientele.
15. Aerial Application Helicopters
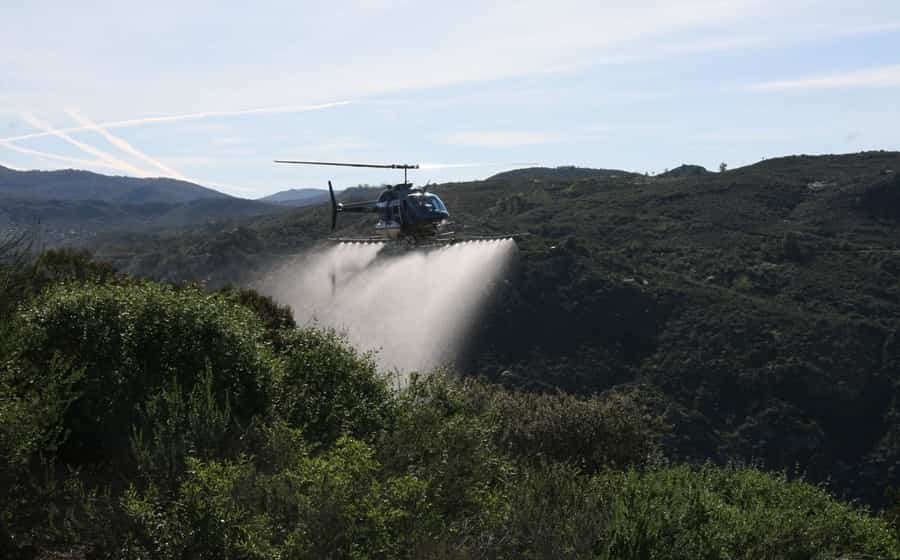

Aerial application helicopters specialize in tasks such as crop dusting, firefighting, and pesticide spraying where precision and agility are essential. They feature specialized equipment and maneuverability for effective aerial operations.
Applications: Integral in agriculture, forestry, and environmental management, these helicopters enhance crop yields, combat wildfires, and control pests without the limitations of ground-based methods. Their versatility supports sustainable practices and emergency response efforts.
Conclusion
This detailed guide explores the diverse capabilities of helicopters across various sectors, showcasing their evolution from basic transport to sophisticated multi-role platforms. Helicopter technology continues to advance, ensuring these aerial assets remain indispensable in addressing complex challenges worldwide.
Suggested to Read:
COMMENTS